
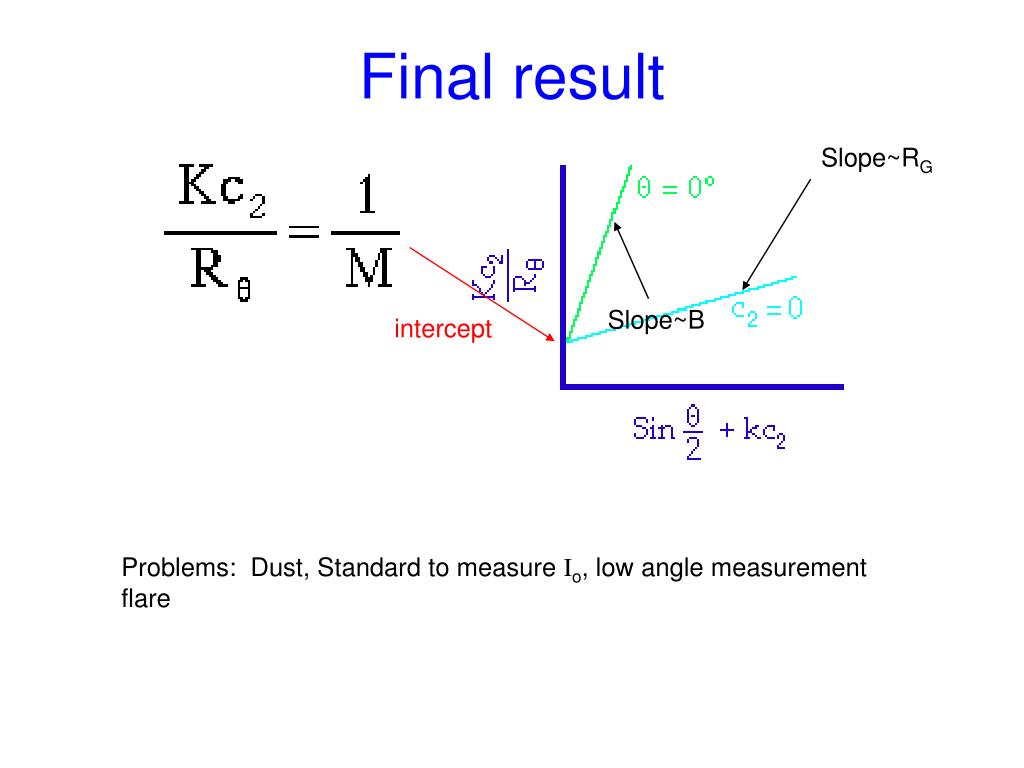
Greater than 0.7 – Very Polydisperse Probably not.The Correlation Function for monodisperse particleĪ = the baseline of the correlation functionī = intercept of the correlation function.ĭ = translational diffusion coefficient, q = scattering vectorĮxpanded to account for polydispersity or band broadening: More extended the decay becomes the greater the polydispesity. The steeper the curve the more mono disperse the sample is. If the particle will large the signal will changes slowly and correlation will sustain Correlation of a signal arriving from random source will decrease with time. Will be a strong correlation between two signal. If the intensity at time t is compared with the intensity at time t+δt, there Of similarity between two signals, or one signal with itself at varying time A correlator is basically a signal comparator. Particles within the sample being measured. Within the correlation curve all of the information regarding the diffusion of A correlation function is statistical correlation between random variables at twoĭifferent points in space or time, usually as a function of the spatial or temporal
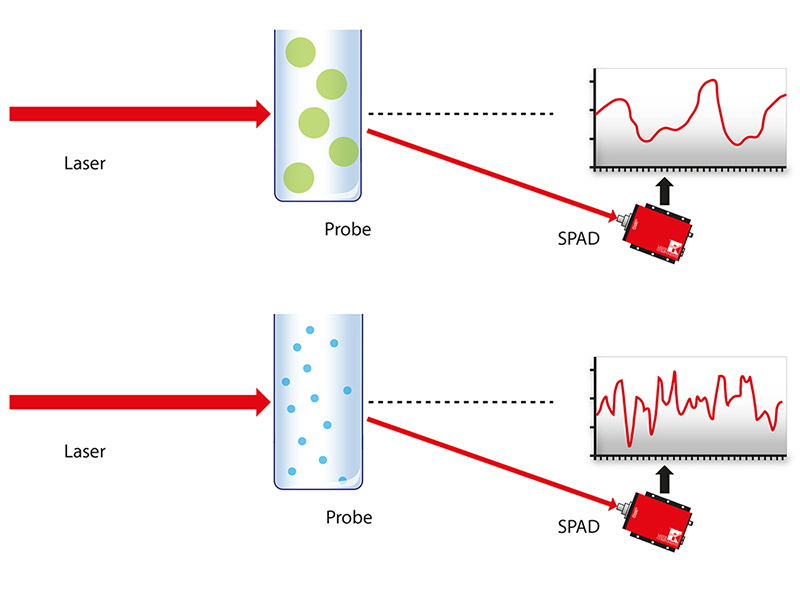
Intensityįluctuations seen through time are therefore slower for large particles. Through a solvent, while small particles diffuse more quickly. Particles with a large physical dimension (radius) diffuse more slowly The “ noise “ is actually the particle motion and will be used to measure the particle Obtained optical signal shows random change due to random change in the It is related to the Viscosity and Temperature. It describes the way in which very small particles move in fluid Brownian motion of the particles are related to size. Brownian motion of the particle is random motion due to theīombardment by the solvent molecule surround them. Brownian motion is the fundamental of this instrument This is done by measuring the rate at which the intensity of the scattered lightįluctuates when detected using a suitable optical arrangement. In DLS, the speed at which the particles are diffusing due to Brownian motion is Sample preparation is not required for the measurement Complete recovery of sample after measurement Good for detecting the aggregation of the particles One can also study stability of nanoparticles as function of time For measuring Hydrodynamic Size of nanoparticle, protein and biomaterial Size distribution, Hydrodynamic radius, Diffusion coefficient So it measure real time intensity, thus measuring the dynamic It measure and interpolate the light scattering up to microsecond. Intensity of light scattered from suspension. Particle size can be determined by measuring the random change in (Diffusion Constant (DT), Size, Rh, Polydispersity Index) Measures Fluctuation Changes on The Intensity of the (Mass(M), Size (rg), Second Virial Coefficient (A2) Measures Total Intensity of Scattered Light


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
